Antitrust Laws and Enforcement Agencies
Unveiling the importance of fair markets, compliance, and innovation. Gain insights into antitrust laws through interactive scenarios, violations, penalties, and best practices.
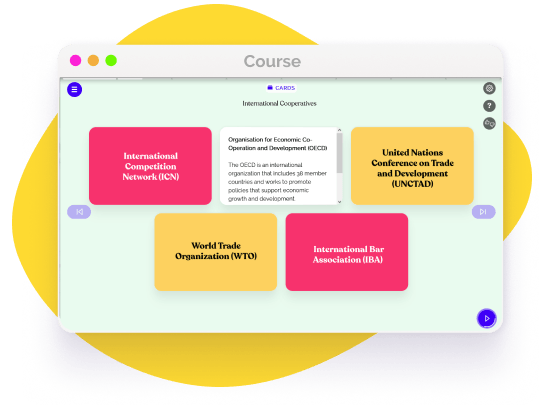
State and Local Laws
In the United States, both federal and state governments maintain antitrust laws, often mirroring each other. State attorneys general and other regulatory agencies are responsible for enforcing state-specific antitrust statutes and regulations. Notably, state antitrust laws may contain distinct provisions or enforcement mechanisms, further shaping the antitrust landscape.
US Antitrust Enforcement Agencies play a pivotal role in upholding fair competition and preventing anti-competitive practices. Understanding the role and authority of these agencies is crucial in comprehending the robust framework in place to safeguard competition and protect consumer interests.
Each state in the United States has its own attorney general's office, which often includes a division dedicated to antitrust enforcement. State attorneys general have the authority to enforce both federal and state antitrust laws within their respective jurisdictions, ensuring compliance and promoting fair competition at the state level.
The Department of Justice (DOJ) enforces antitrust laws by scrutinizing and, if necessary, prosecuting businesses that engage in anticompetitive practices. The DOJ's Antitrust Division investigates potential violations, such as price fixing, bid rigging, market allocation, and monopolistic behavior. Through legal action and collaboration with other enforcement agencies, the DOJ plays a vital role in maintaining a competitive and fair marketplace, safeguarding consumer interests, and promoting economic growth.
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is crucial in enforcing antitrust laws by investigating and challenging business practices that may restrain competition or harm consumers. The FTC uses its authority to prevent mergers and acquisitions that may create monopolies or stifle competition and take legal action against companies that engage in unfair, deceptive, or anticompetitive practices.

Antitrust Penalties For Organizations
Organizations found guilty of violating antitrust laws face serious penalties. These include financial penalties, which can be substantial and even debilitating. Organizations can also face civil damages and follow court orders to stop certain actions. In some cases, companies may be required to divest assets or take specific actions to restore market competition, which can significantly impact operations and market position.
Antitrust Penalties For Individuals
Individuals are not immune to penalties if found guilty of violating antitrust laws. Here are some penalties someone would face if they violated antitrust laws:
Here are some myths to look out for:
- -
Individuals involved in antitrust violations can face criminal charges. In the US, under the Sherman Act, individuals can be fined and face imprisonment.
- -
Individuals found guilty of antitrust violations may be barred from serving as directors or holding certain positions within a company for a specified period.
- -
Individuals can be held personally liable for civil damages resulting from antitrust violations.

Navigate the Complexities of Business Compliance with Antitrust Training
Antitrust training helps businesses navigate compliance complexities by providing a comprehensive understanding of antitrust laws. Through interactive learning, professionals gain insights into regulations, prohibited practices, and enforcement mechanisms, enabling them to mitigate legal risks and foster a culture of compliance.
Helping over 8,000 organizations create a safer, more productive workplace
Dive into the world of antitrust laws, analyzing the agencies that regulate them, common antitrust violations and violation penalties, and best practices for remaining in compliance. This course covers: