How and When to use PHI in relation to HIPAA Laws
Private Health Information (PHI) can be used for a variety of reasons without authorization. For instance, healthcare providers can freely use PHI to facilitate treatment, for payment processing, and for healthcare operations, which are commonly referred to collectively as TPO.
When is PHI mandatory to Report?
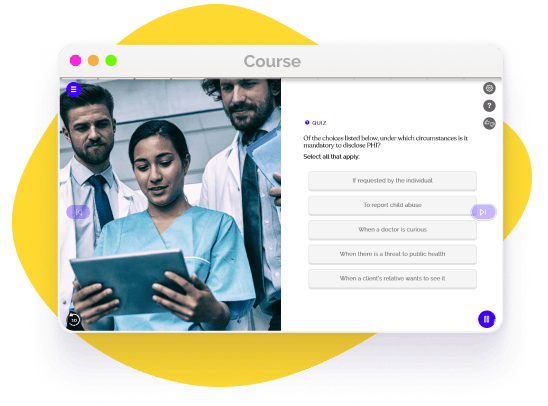
If people request information from their record, as a covered entity, you must disclose the information, unless an exception applies. Another mandatory disclosure is to the Department of Health and Human Services, for a compliance investigation. Sometimes, disclosures of PHI are required by law; common reasons can include reporting vulnerable adult abuse, reporting child abuse, when there is a court order signed by a judge, when there is a threat to public health, and sometimes for disaster relief purposes and to report vital statistics to the government.
Using PHI to Process Healthcare Payments
In this chapter, we’ll take a closer look at some of the healthcare business operations where a healthcare provider has the right to use and disclose PHI. For example, healthcare providers are free to use PHI to process healthcare payments. However, if an individual has paid out of pocket in full for the medical services they receive, they have the right to restrict disclosure to the health plan provider.
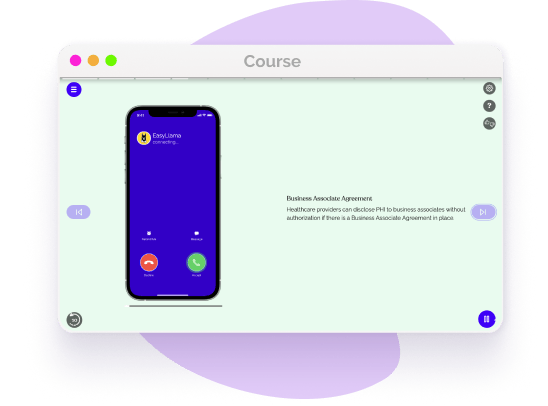
PHI can be used without authorization to facilitate treatment, for payment processing, and to conduct healthcare business operations.
For instance, you may disclose PHI to Business Associates without authorization if you have a business associate agreement in place. An informal authorization is acceptable in the case of discussing treatment and outcomes or payment with the individual’s caretaker who could be a friend or family member when the information is directly relevant to this person’s involvement with the individual’s care.
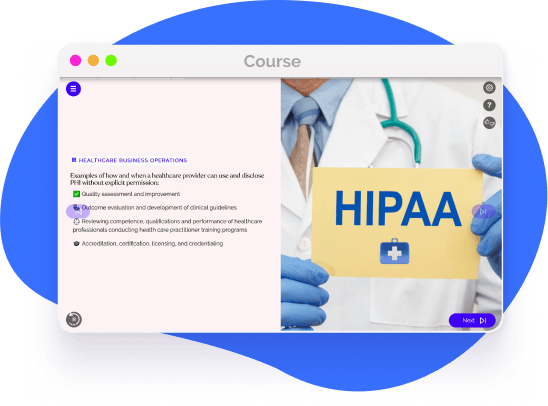
Some examples of such operations are a variety of activities of a covered entity including, but not limited to: quality assessment and improvement, outcome evaluation and development of clinical guidelines, reviewing competence, qualifications, and performance of healthcare professionals conducting health care practitioner training programs, accreditation, certification, licensing, and credentialing.
If the individual is incapacitated and there is no authorized representative, medical professionals may use their professional judgement and ethics in determining what information to disclose. It is possible for PHI to be disclosed to the personal representative of the individual, if: The individual’s representative’s identity is verified and proper procedures are followed for a response to a request for access.
Disclosing PHI without Explicit Permission
A healthcare provider has the right to use and disclose PHI without explicit permission for a variety of business activities. Examples of these activities include but are not limited to:
Here are some myths to look out for:
- -
Quality assessment and improvement
- -
Outcome evaluation and development of clinical guidelines
- -
Reviewing competence, qualifications, and performance of healthcare professionals conducting health care practitioner training programs
- -
Accreditation, certification, licensing, and credentialing

HIPAA Training to Benefit your staff members
The primary benefit of HIPAA training that includes private health information is that it helps ensure that healthcare providers, staff, and other individuals who handle private health information are aware of their obligations to protect the privacy and security of patients’ data. EasyLLama’s HIPAA training courses for Business Associates and Covered Entities helps ensure that all healthcare professionals are familiar with the rules and regulations set forth by HIPAA and that they understand the importance of protecting patient privacy.
Helping over 8,000 organizations create a safer, more productive workplace
EasyLlama’s online training course helps prepare employees to navigate HIPAA. This course provides an in-depth examination of how to respond to a breach of confidential data and the best way to protect your patients. The course covers: