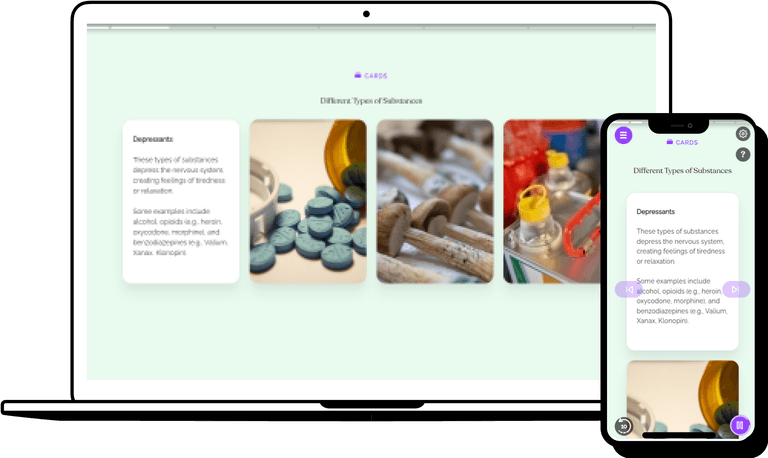
Substance Use Disorders (SUDs)
Discover insights into the impact of substance use disorders on campus, and how to create a safe and healthy environment for everyone.
When Substance Use Becomes Substance Use Disorder
When substance abuse develops into a disorder, it ceases to be a voluntary behavior, and the user loses control over their usage. They may have strong desires for the drug and struggle to cut back despite the damaging consequences it has on their relationships, employment, and overall health.

In order to better understand how drug use disorder develops, scientists and medical professionals developed the biopsychosocial model in addition to the illness model of the condition. It incorporates biological components, just like the disease model, but it also takes into account psychological, cognitive, social, cultural, and environmental factors.
Things including a person's surroundings, family, and peers are sociological elements that can contribute to the development of an SUD.
Peer pressure and traumatic events are examples of psychological influences. Moreover, factors including mental discomfort, anxiety, and despair may also help an SUD develop. Many people who have substance use disorders also co-occur with a mental disease, such as bipolar disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, major depressive disorder, or an anxiety disorder.
Neurological variables, brain chemistry, and genetics are examples of biological factors that affect SUD. According to research, a person's chance of acquiring an SUD may be influenced by their genes to an extent of up to 50%.

Common Misunderstandings About SUDs
It's a common misconception that people with substance use disorders (SUDs) have a moral shortcoming or are "weak-willed" because they can't stop using drugs or alcohol on their own. In actuality, SUDs are complicated medical diseases that can be brought on by a number of variables, including a person's environment, heredity, or even a combination of both.
Examples of SUDs and Associated Substances
The overuse of substances including alcohol, cocaine, and other substances falls under the umbrella of a collection of mental health illnesses known as substance use disorders (SUDs). Look at a few instances:
Here are some myths to look out for:
- -
Opioid Use Disorder : Heroin, hydrocodone (e.g., Vicodin), oxycodone (e.g., Oxycontin, Percocet), morphine, codeine, fentanyl
- -
Alcohol Use Disorder : Beer, wine, liquor, etc.
- -
People who use substances are criminalsCannabis Use Disorder : Marijuana and marijuana-related products
- -
Stimulant Use Disorder with a Amphetamine-Type Substance : Methamphetamine, sometimes called meth, and amphetamine, sometimes called speed

Discover the impact of SUDs On Campus through Online education
Uncover the profound consequences of Substance Use Disorders (SUDs) within the campus community through our online education platform. Gain valuable insights into the far-reaching effects of SUDs on individuals, relationships, and academic success. With the convenience of online learning, delve into the complexities of addiction, prevention strategies, and support mechanisms.

Helping over 8,000+ organizations create a safer, more inclusive company culture
EasyLlama’s online training course provides a more in-depth understanding of substance use and misuse on campus. Explore how to identify signs of substance misuse in themselves, their colleagues, and their students and address these issues in a supportive and non-judgmental manner. The course covers: